Lazarus Security Lab’s findings reveal protocol-level controls across major networks, challenging the core principles of blockchain autonomy.
Bybit’s Study Exposes Fund-Freezing Functions Across 16 Blockchains
A new report from Bybit’s Lazarus Security Lab has found that 16 major blockchain networks possess the technical ability to freeze or restrict user funds, sparking renewed debate about decentralization and user control in digital asset systems.
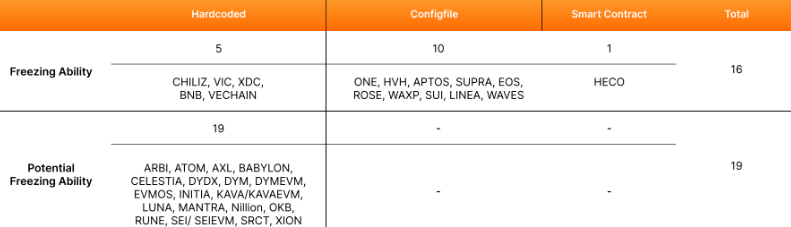
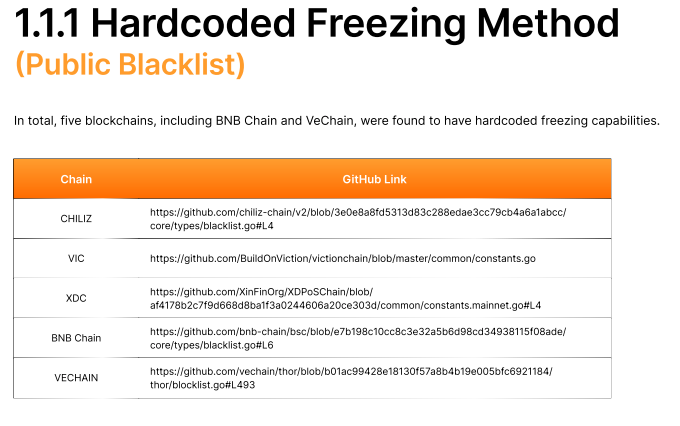
After analyzing 166 blockchain networks, the research team discovered that several—including BNB Chain, VeChain, and Sui—feature protocol-level mechanisms allowing developers, validators, or foundations to halt specific transactions or addresses.
“Even when designed to enhance security or prevent theft, these mechanisms raise fundamental questions about censorship resistance and decentralization,” the researchers noted in the report.
Three Mechanisms Behind Fund Freezing
The Bybit security team identified three distinct freezing methods across affected blockchains:
- Hardcoded Freezing / Public Blacklists – Embedded directly into the network’s source code, enabling developers to freeze wallets or tokens.
- Networks: BNB Chain, VeChain, Chiliz, Viction, and XinFin’s XDC Network.
- Configuration File-Based Freezing / Private Blacklists – Managed via local configuration files like YAML, ENV, or TOML, typically controlled by validators or core teams.
- Networks: Aptos, EOS, and Sui, among others.
- Onchain Smart Contract Freezing – Deployed via smart contracts that can manage or restrict specific addresses.
- Example: Heco Chain (Huobi Eco Chain), which uses an onchain contract for blacklisting.
The researchers found that 10 of the 16 chains rely on configuration-based methods, while five include freezing directly in their source code.
Potential for More Chains to Adopt Freeze Controls
The study also highlighted 19 additional blockchains, particularly within the Cosmos ecosystem, that could easily implement freezing features through minor protocol changes.
The report drew attention to Cosmos’ module accounts, which operate under module logic instead of private keys, allowing developers to modify or restrict transaction behavior.
“Implementing such a change would require a hard fork and minor code adjustments — likely in the anteHandler file,” the report explained, adding that none of the Cosmos-based chains currently use this for fund control.
Security vs. Censorship: The Growing Trade-Off
While fund-freezing capabilities can aid in recovering stolen assets or preventing fraud, the Lazarus team warned that their existence could centralize power and undermine blockchain neutrality.
This revelation follows Bybit’s $1.5 billion cold wallet hack earlier this year, during which coordinated action with Circle, Tether, THORchain, and Bitget helped freeze roughly $42.9 million in stolen assets.
The incident underscores a complex tension: the desire for decentralized freedom versus the need for centralized security controls.
The findings from Bybit’s Lazarus Lab mark a pivotal moment for blockchain governance. As networks increasingly embed emergency controls and compliance modules, the crypto industry faces a fundamental question — can true decentralization coexist with administrative safeguards?
Disclaimer
This content is for informational purposes only and does not constitute financial, investment, or legal advice. Cryptocurrency trading involves risk and may result in financial loss.

