The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has issued new guidance on tokenized securities, distinguishing between issuer-sponsored and third-party models. The move clarifies that blockchain issuance does not exempt securities from federal regulations.
Issuer-Sponsored Tokenized Securities
Issuer-backed tokens allow companies to tokenize their own securities, either by updating ownership records directly on-chain or issuing crypto assets that trigger off-chain ledger updates. The SEC emphasized that all traditional securities laws, including registration requirements, still apply regardless of the issuance format.
Securitize said in a post to X on Wednesday;
Third-Party Tokenization
Third-party models involve custodial or synthetic structures. In the custodial model, tokens represent indirect ownership of underlying securities held in custody. The synthetic model issues new instruments linked to securities, such as structured notes or security-based swaps. The SEC warned that holders may face risks if the third party defaults, reinforcing a preference for broker-led custody over crypto-native self-custody.
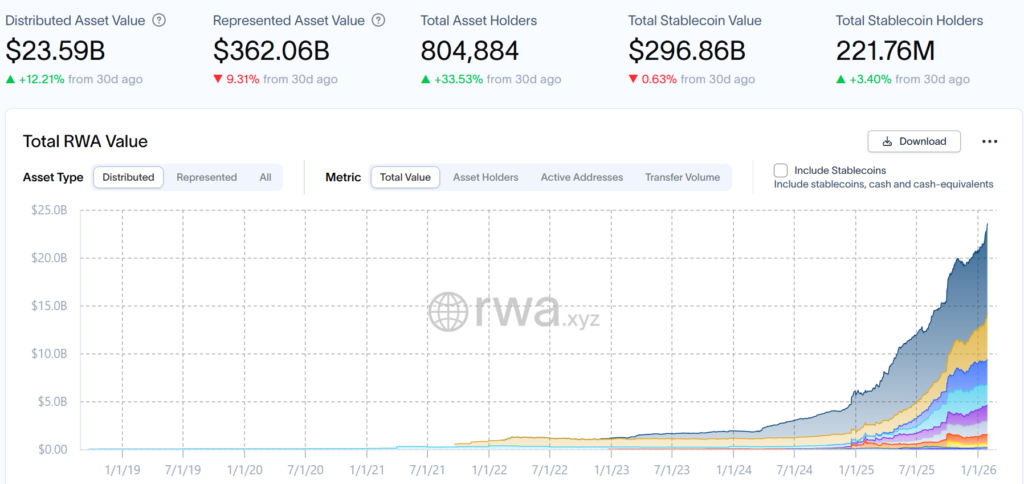
The SEC’s guidance confirms that blockchain is a record-keeping tool, not a way to bypass regulations. The Depository Trust and Clearing Corporation (DTCC) may now move certain stocks, bonds, and U.S. Treasuries on-chain, marking a step toward integrating tokenized real-world assets within regulated markets.
By distinguishing between issuer and third-party tokenization, the SEC provides a clearer framework for compliant blockchain-based securities, supporting responsible growth in tokenized financial markets.
Disclaimer
This content is for informational purposes only and does not constitute financial, investment, or legal advice. Cryptocurrency trading involves risk and may result in financial loss.

